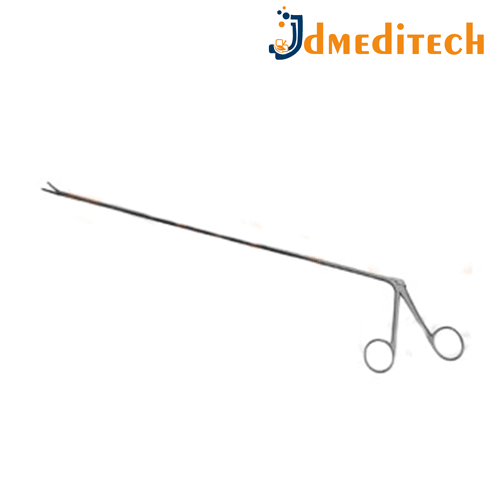
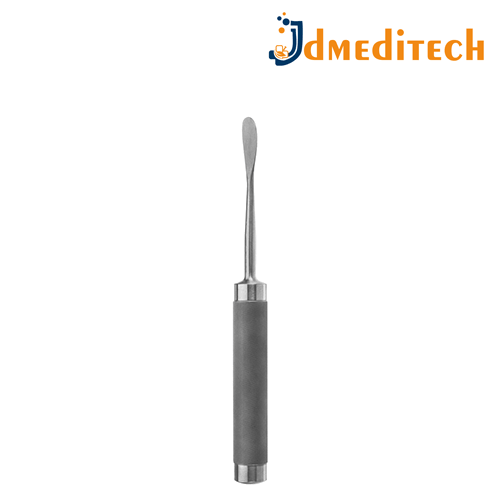
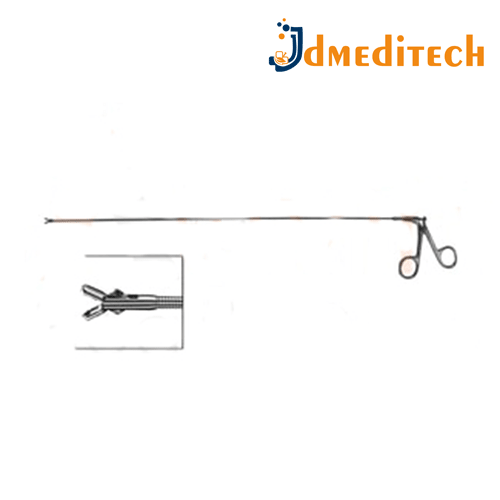
Neuro Endoscope Grasping Forceps are precision surgical instruments used in neuroendoscopic procedures to hold, manipulate, or remove tissue or foreign bodies from within the brain or spinal canal.
Features:
Long, slender design to fit through the working channel of a neuroendoscope
Fine, serrated or toothed jaws for secure gripping
Made from high-grade stainless steel
Rigid or semi-flexible options available
Ergonomic handle for precise control
Uses:
Grasping and removing tissue or biopsy samples
Handling foreign bodies or small instruments during brain surgery
Assisting in endoscopic tumor resection or cyst fenestration
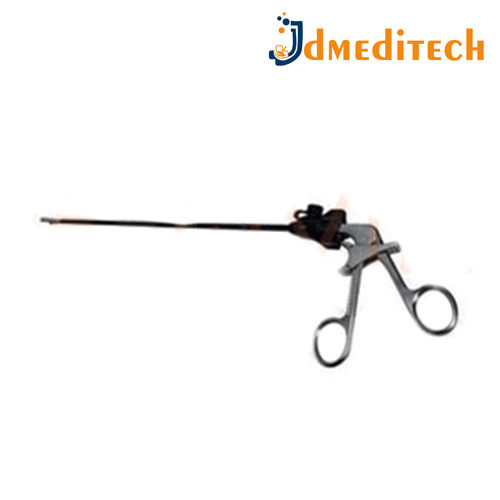
Neuro Endoscope Biopsy Forceps are specialized surgical instruments used during neuroendoscopic procedures to obtain tissue samples (biopsies) from within the brain or spinal cord.
Features:
Slim and elongated design to pass through a neuroendoscope’s working channel
Precise jaw control for accurate tissue grasping and cutting
Available in rigid or flexible versions
Made of biocompatible stainless steel or high-grade surgical alloys
Uses:
To extract tissue samples for diagnostic purposes (e.g., tumors, cysts, lesions)
Commonly used in:
Intraventricular tumor biopsies
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) with biopsy
Minimally invasive brain procedures
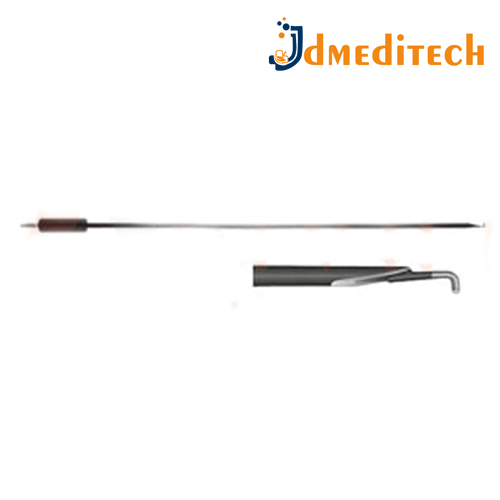
Ventriculoscope Bipolar Probe is a specialized neurosurgical instrument used in neuroendoscopic procedures to coagulate (stop bleeding) within the brain’s ventricular system.
Features:
Designed for use through the working channel of a ventriculoscope
Bipolar coagulation ensures precise control with minimal heat spread
Slender and flexible shaft for maneuverability in narrow intracranial spaces
Compatible with standard bipolar electrosurgical units
Uses:
Hemostasis (control of bleeding) during endoscopic brain surgeries
Coagulating blood vessels or tissue in procedures like:
Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV)
Tumor resection
Cyst removal
Ventriculoscope Grasping Forceps are specialized surgical instruments used during neuroendoscopic procedures involving the brain’s ventricular system.
Features:
Long, slender design compatible with a ventriculoscope
Precision-crafted jaws for accurate tissue grasping
Typically made from high-grade stainless steel
Designed for smooth insertion through the endoscopic working channel
Uses:
To grasp, manipulate, or remove tissue within the brain ventricles
Commonly used in cyst removal, tumor biopsy, or foreign body extraction
Helps perform delicate maneuvers with minimal trauma during neuroendoscopy
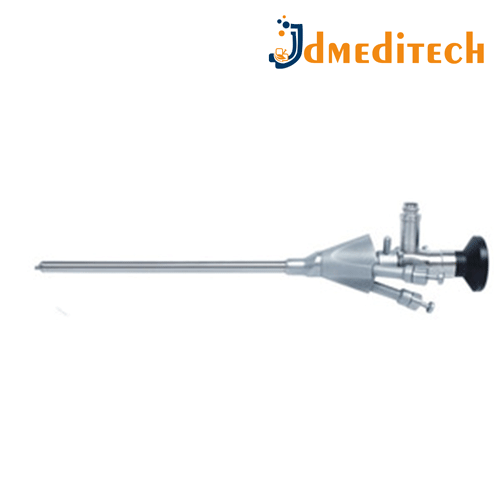
Ventriculoscope Sheath is a specialized surgical accessory used in neuroendoscopy.
Features:
A protective tubular sheath that houses the ventriculoscope
Made of durable, biocompatible material
Designed to fit snugly and allow smooth insertion into brain ventricles
Provides channels for irrigation and instrument passage
Uses:
Protects brain tissue during insertion of the ventriculoscope
Maintains a clear pathway for visualization inside the brain ventricles
Facilitates procedures like ventriculostomy, cyst removal, and biopsy
Helps in safe, minimally invasive neurosurgical interventions
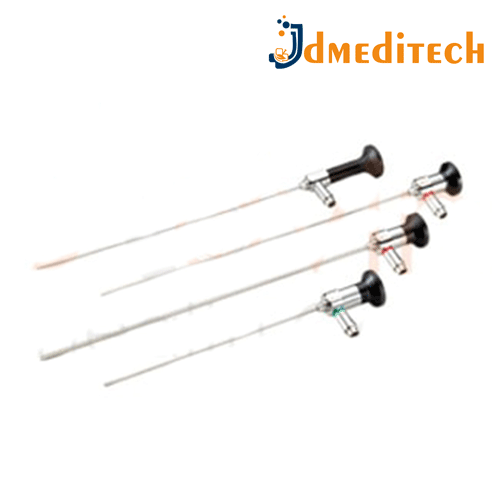
Encephaloscope is a specialized endoscopic instrument designed for minimally invasive brain surgeries.
Features:
Thin, rigid or flexible tube with a camera and light source
Provides clear visualization inside the brain or ventricular system
Small diameter for minimal tissue damage
May have working channels for surgical tools
Uses:
Used in neurosurgery to examine and treat brain ventricles and lesions
Helps in procedures like ventriculostomy, tumor biopsy, cyst removal
Allows surgeons to operate with minimal invasion, reducing recovery time and complications
A Spinal Needle is a thin, hollow needle used to access the subarachnoid space in the lower spine, primarily for spinal anesthesia, diagnostic lumbar punctures, or intrathecal drug delivery.
Features:
Fine, long shaft with sharp beveled tip
Stylet inside to prevent tissue clogging
Available in various gauges and lengths
Uses:
Administer spinal anesthesia during surgeries
Collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing
Deliver chemotherapy or pain medications intrathecally
A Spine Elevator is a surgical instrument used in spinal surgeries to gently lift, separate, or elevate soft tissues or bone structures such as vertebrae, muscles, or ligaments. It provides access and visibility to deeper spinal structures without causing damage.
Features:
Made of stainless steel
Available in various tip shapes (curved, straight, or angled)
Ergonomic handle for controlled use
Uses:
Elevate periosteum or soft tissues during dissection
Assist in laminectomy, discectomy, and spinal fusion
Create space for inserting implants or instruments
Spine Grasping Forceps are specialized surgical instruments used during spine surgeries—particularly in minimally invasive or endoscopic spine procedures—to hold, manipulate, or remove tissues like disc material or bone fragments.
Features:
Long, slender design for deep access
Fine, serrated or fenestrated tips for secure grip
Made of medical-grade stainless steel
Available in straight or curved versions for different angles
Uses:
Grasp and remove herniated disc fragments
Hold soft tissue during discectomy or decompression
Aid in precision handling of tissues near spinal nerves
A Spine Sheath is a specialized surgical instrument used in minimally invasive spine procedures, especially during endoscopic or spinal decompression surgeries.
Features:
Made from medical-grade stainless steel or composite material
Comes with an outer sheath and inner working channel
Allows insertion of endoscopic instruments (e.g., camera, grasper)
Often designed with side ports for irrigation or suction
Uses:
Provides a working tunnel to access the spine safely
Maintains a clear surgical field by managing fluid flow
Minimizes tissue trauma in endoscopic discectomies, foraminotomies, and other spine surgeries