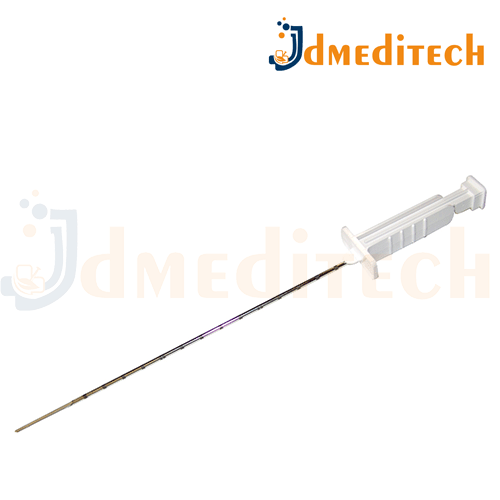
A Biopsy Needle is a medical instrument used to extract a tissue sample from the body for diagnostic examination, typically to detect cancer, infection, or other abnormal conditions.
Key Features:
Sharp, hollow needle for penetrating tissue and extracting a sample
Various types (core needle, fine needle, vacuum-assisted) for different procedures
Ergonomic handle for precise control
Sterile, single-use or reusable depending on type
Graduated markings to guide insertion depth
Some may have spring-loaded mechanisms for automatic sampling
Uses:
Collect tissue samples from organs such as the liver, breast, kidney, prostate, or bone marrow
Aid in the diagnosis of tumors, infections, and inflammatory conditions
Minimally invasive alternative to surgical biopsies
Commonly used in radiology, oncology, and urology
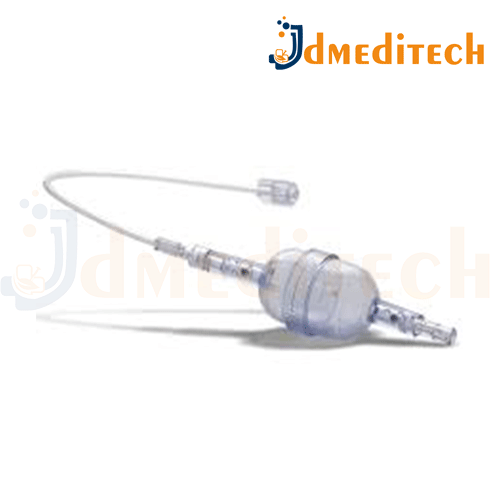
The Path Finder is a specialized urological instrument used during endoscopic procedures (like ureteroscopy or TURP). Its primary function is to provide controlled irrigation — that is, the flushing of sterile fluid — to keep the surgical area clear of blood, tissue, or debris for better visualization and precise work by the surgeon.
It is manufactured and exported by JDMeditech, a medical device company based in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India.
Key Features:
Controlled Irrigation: Ensures a steady or pulsatile flow of fluid during endoscopy.
Enhanced Visualization: Clears the view for surgeons by washing away obstructions.
Continuous or Bolus Flow: Offers flexibility for different surgical needs.
User-Friendly Design: Easy to handle and connect with standard urological equipment.
Reusable or Disposable Options: Available in both formats for hospital requirements.
Compact and Durable: Designed for reliable performance during procedures.
Uses in Medical Procedures:
Endoscopic Urological Surgeries: Such as TURP (Transurethral Resection of the Prostate), ureteroscopy, or bladder tumor removal.
Flushing Ureteral Tracts: To remove blood, tissue fragments, or clots.
Maintaining Clear View: Essential for high-precision work inside narrow urinary passages.
Supporting Diagnostic Procedures: Like cystoscopy or ureterorenoscopy.
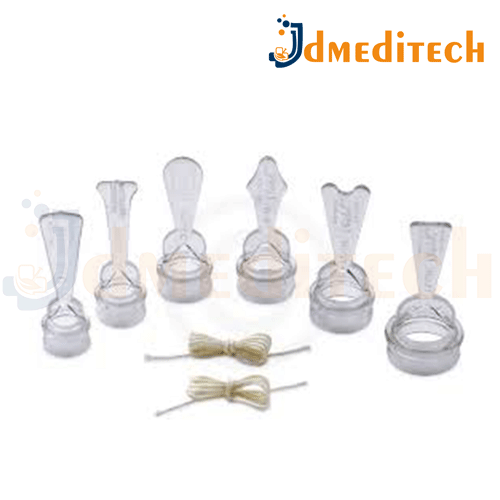
The Plastibell Circumcision Device is a small, clear plastic ring used to perform circumcision in newborn male infants. It’s a safe, commonly used method that involves placing the ring over the glans of the penis and tying a ligature around the foreskin to cut off its blood supply. Over a few days, the foreskin falls off along with the ring—usually within 5 to 10 days.
Key Features of the Plastibell Device:
Material – Clear medical-grade plastic, non-toxic and disposable.
Sizes – Available in various sizes to fit different newborn anatomy.
Ligature Groove – Special groove to hold the surgical string in place securely.
Bloodless Procedure – The tight ligature reduces or eliminates bleeding.
Stitch-Free – No need for sutures or surgical closure.
Self-Removing – The ring falls off naturally as healing progresses.
Minimally Invasive – Simple, quick outpatient procedure (often under 10 minutes).
Used In:
Newborn Male Circumcision (most common use)
Infants up to a few months old
In clinics, hospitals, or pediatric surgical centers
Preferred when parents choose religious, cultural, or medical circumcision
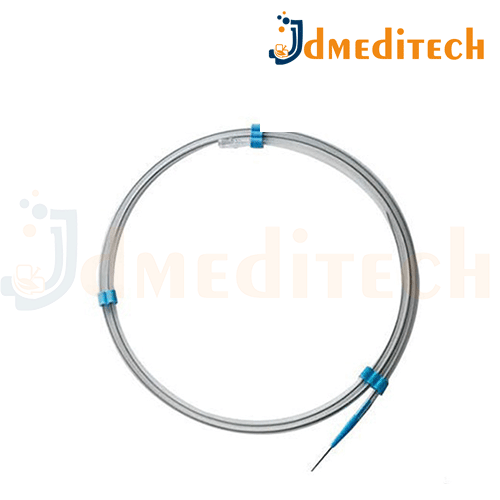
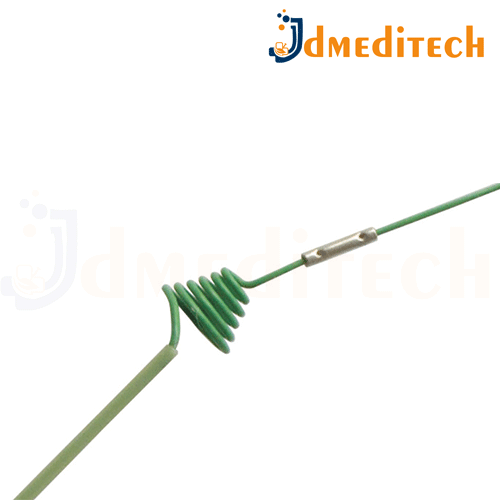
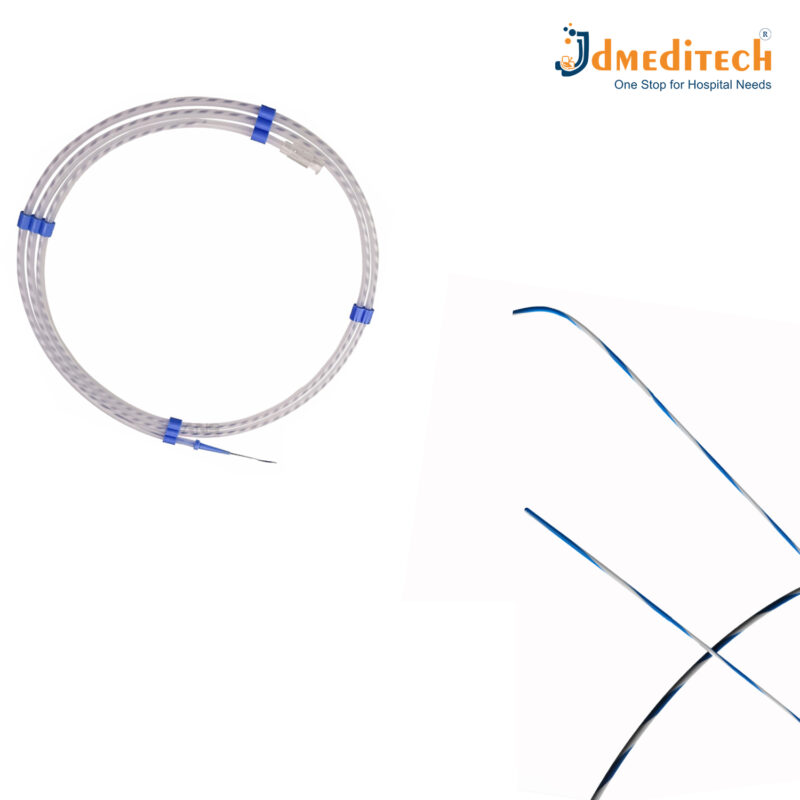
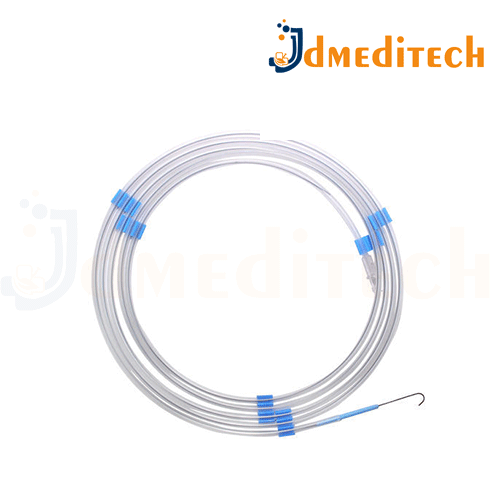
A Zebra Guide Wire is a specialized guide wire used in minimally invasive medical procedures, designed for precise navigation through body cavities such as blood vessels, urinary tract, or gastrointestinal system. It features a distinct striped or “zebra” pattern on its surface, which helps with visibility under imaging techniques (like fluoroscopy).
Key Features:
Zebra-striped design for easy visual identification under X-ray or fluoroscopy
Flexible and durable structure, often made from stainless steel or Nitinol
Radiopaque tip for better visualization in imaging systems
Smooth surface for reduced friction and easier navigation
Variety of sizes and lengths to suit different medical procedures
Shape-memory properties (in some versions) for flexibility and straightening after bending
Uses:
Guidewire for catheter insertion in angioplasty, stent placement, and balloon procedures
Urological interventions, like ureteroscopy and kidney stone removal
Cardiovascular procedures, such as coronary artery interventions
Gastrointestinal procedures involving guidewire-assisted insertion of endoscopes or stents
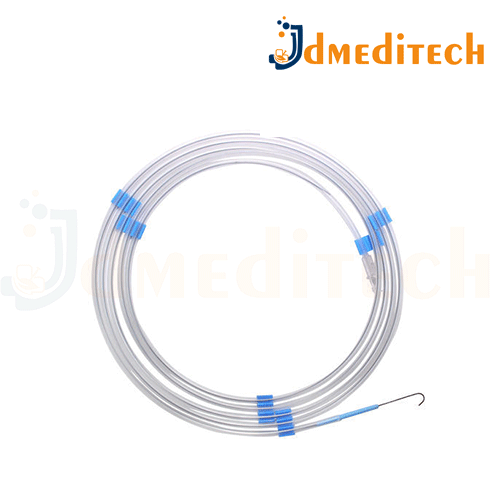
A Nitinol Guide Wire is a thin, flexible wire made from Nitinol, a type of shape-memory alloy that is commonly used in minimally invasive medical procedures to guide instruments through blood vessels, ducts, or other body pathways.
Key Features:
Made of Nitinol alloy (a blend of nickel and titanium) for flexibility and shape memory
Highly flexible yet strong, enabling it to bend around curves without kinking
Shape-memory properties allow it to return to a pre-determined shape after bending
Radiopaque tip for easy visibility under X-ray
Variety of lengths and diameters for different procedures
Coated or uncoated versions for smoother navigation
Uses:
Guide catheter placement in procedures like angioplasty or stent insertion
Urinary tract procedures (e.g., ureteroscopy, kidney stone removal)
Vascular interventions (e.g., coronary or peripheral interventions)
Minimally invasive surgeries requiring precise navigation
A hydrophilic guidewire is a specialized medical wire coated with a hydrophilic (water-attracting) polymer that becomes very slippery when wet. It is used to guide catheters or other instruments safely through narrow, curved, or difficult pathways in the body during procedures like angioplasty, urology, or endoscopic surgeries.
Key Features of a Hydrophilic Guidewire:
Hydrophilic Coating – Becomes super-slippery when wet, reducing friction and making navigation easier.
Flexibility – Easily bends through twisted or narrow anatomical passages.
Atraumatic Tip – Soft, tapered tip minimizes tissue injury and ensures gentle passage.
Radiopacity – Often contains radiopaque markers so it’s visible under X-ray or fluoroscopy.
Excellent Trackability – Follows the path of least resistance, ideal for tight spaces.
Disposable – Usually single-use to ensure sterility and performance.
Common Uses:
Urology: Navigating the ureters for stent or catheter placement.
Cardiology: During angioplasty to cross blockages in blood vessels.
Gastroenterology: For accessing the bile or pancreatic ducts (e.g. ERCP).
Interventional Radiology: To assist in vascular access or drainage procedures.
A PTFE guide wire is a thin, flexible medical wire coated with Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)—commonly known as Teflon. It is used to guide catheters, stents, or other medical devices safely through blood vessels, urinary tracts, or body ducts during minimally invasive procedures such as angioplasty, catheterization, or urological surgeries.
Key Features of PTFE Guide Wire:
PTFE Coating (Teflon) – Offers a smooth, slippery surface for low-friction navigation.
Flexibility – Allows safe movement through curved or delicate anatomy.
Strength and Torque Control – Provides enough stiffness for control while resisting kinks or bends.
Radiopacity – Many are visible under X-ray or fluoroscopy for accurate placement.
Non-reactive Material – PTFE is biocompatible and non-toxic, reducing risk of irritation.
Hydrophobic – Resists sticking to moist tissues, reducing trauma during insertion.
Common Medical Uses:
Cardiology: To guide catheters during angioplasty or stent placement.
Urology: For ureteral stent placement, nephrostomy access, or stone retrieval.
Interventional Radiology: To access blood vessels or ducts for drainage or biopsy.
Types of PTFE Guide Wires:
Straight tip or angled tip – depending on the anatomy and required direction.
Standard or hydrophilic-coated – some include extra coatings for even smoother navigation.
A PCN Basket is a specialized urological device used during Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) procedures to retrieve kidney stones or fragments after they are broken down through lithotripsy.
Features:
Flexible or semi-rigid shaft for easy navigation
Nitinol or stainless steel wire basket for stone capture
Atraumatic tip to minimize tissue damage
Radiopaque markers for visibility under fluoroscopy
Compatible with PCNL sheaths
Uses:
Stone retrieval during PCNL surgeries
Helps in extracting stone fragments after lithotripsy
Effective for removal of larger stones from the kidney or renal pelvis
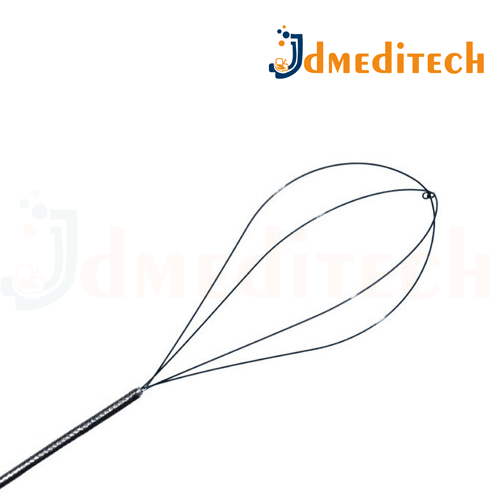
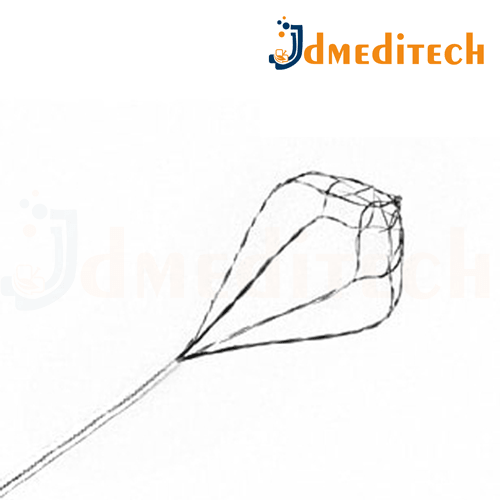
A Spider Basket is a flexible urological retrieval device with multiple wire arms, designed to grasp and remove urinary stones or foreign bodies from the kidney, ureter, or bladder.
Features:
Multi-wire design (often 6 or more wires) for better grip
Made from Nitinol or stainless steel
Flexible shaft to navigate urinary tract easily
Atraumatic tips for minimal tissue damage
Available in various sizes and configurations
Uses:
Ideal for capturing and extracting small or fragmented stones
Used during URS, PCNL, or cystoscopy procedures
Effective in tight or curved areas due to its flexibility
A Stone Cone Basket is a specialized urological device designed to prevent stone migration during ureteroscopic lithotripsy (stone-breaking procedures), and to retrieve fragments afterward.
Features:
Cone-shaped nitinol basket that acts as a barrier
Prevents retropulsion (stone moving back toward the kidney)
Flexible and atraumatic for safe use in the ureter
Radiopaque marker for accurate placement under imaging
Can also assist in stone fragment retrieval
Uses:
Used during ureteroscopic lithotripsy to trap and prevent stones from moving upward
Helps in safe retrieval of stone fragments
Enhances the success of stone removal procedures