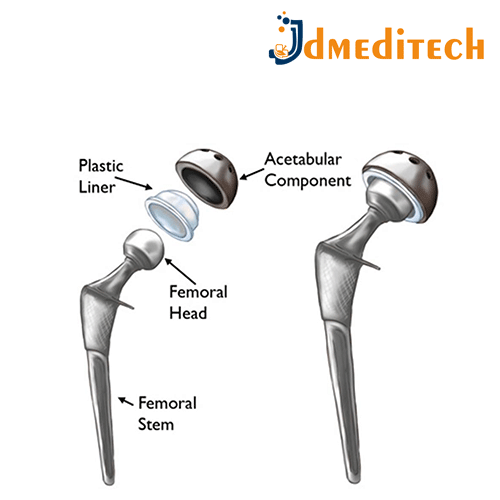
Hip implants are medical devices used to replace or repair the hip joint, commonly during total or partial hip replacement surgeries. They restore mobility and relieve pain caused by arthritis, fractures, or other joint damage.
Key Components:
Femoral Stem: inserted into the thigh bone (femur)
Femoral Head: replaces the ball at the top of the femur
Acetabular Cup: fits into the hip socket
Liner: sits inside the cup to reduce friction
Materials:
Titanium or stainless steel (metal parts)
Polyethylene or ceramic (liner/head)
Uses:
Treat severe osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
Repair hip fractures
Address joint deformities or degeneration
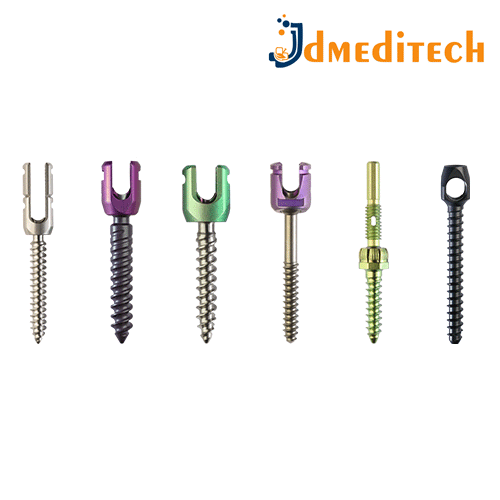
Spine implants are medical devices surgically placed in the spine to stabilize, support, or correct spinal conditions such as fractures, deformities, or degenerative disc disease.
Features:
Made from biocompatible materials like titanium or PEEK
Types include rods, screws, cages, plates, and artificial discs
Designed to promote fusion or replace damaged structures
Uses:
To stabilize spinal segments
Facilitate spinal fusion
Correct deformities like scoliosis
Relieve nerve compression
A PTBD Catheter (Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage Catheter) is a medical device used to drain bile from the liver when the bile ducts are blocked.
Features:
Made of flexible, biocompatible material (usually polyurethane)
Inserted through the skin and liver into the bile ducts
Side holes for effective bile drainage
Radiopaque for X-ray guidance
Available in different sizes and lengths
Uses:
Used in cases of biliary obstruction due to tumors, stones, or strictures
Helps relieve jaundice and prevent infection (cholangitis)
Temporary drainage before surgery or stenting
Used under imaging guidance (ultrasound/fluoroscopy)
A Naso-Jejunal Feeding Tube (NJ Tube) is a thin, flexible tube inserted through the nose that extends into the jejunum (part of the small intestine) to provide nutritional support.
Features:
Made of soft, flexible material (silicone or polyurethane)
Longer than nasogastric tubes to reach the jejunum
Radiopaque for X-ray confirmation
Multiple side holes for feeding
Usually has a small diameter for patient comfort
Uses:
Provides enteral nutrition when stomach feeding is not possible or safe
Used in patients with gastric emptying problems, pancreatitis, or high risk of aspiration
Bypasses the stomach to reduce nausea and reflux
Temporary or long-term feeding support
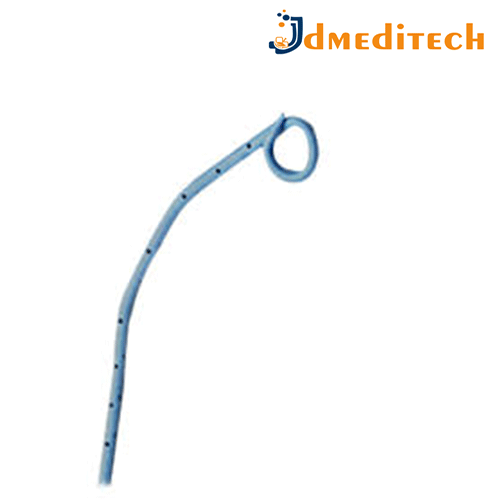
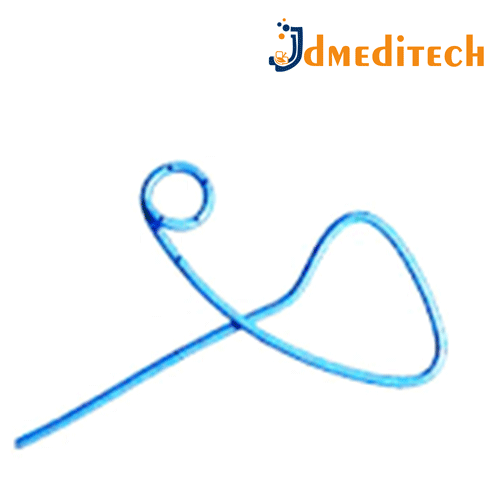
A Naso-Biliary Drainage Catheter is a thin, flexible tube used to drain bile from the liver and bile ducts through the nose in cases of biliary obstruction.
Features:
Inserted through the nose, passes down to the bile duct
Made of soft, flexible material (usually polyurethane)
Has multiple side holes for effective drainage
Radiopaque for visibility on X-ray
Comes with connectors for external bile collection
Uses:
Drains bile in conditions like bile duct stones, tumors, or strictures
Used after ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography)
Helps reduce jaundice and prevent infections (cholangitis)
Temporary support before surgery or stenting
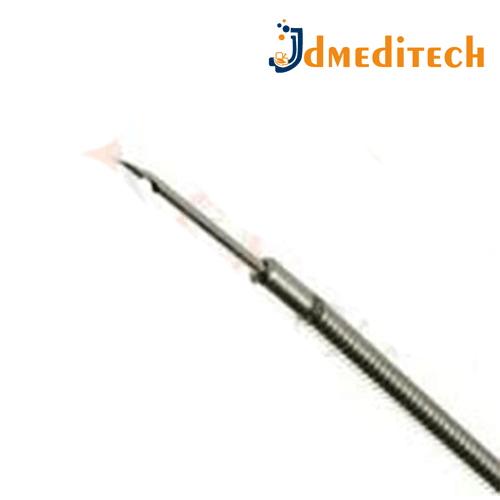
An Endoscopic Aspiration Needle is a specialized needle used in gastrointestinal endoscopy for fine-needle aspiration (FNA) of lesions or masses within or adjacent to the GI tract.
Key Features:
Stainless steel or nitinol needle: Provides strength and flexibility.
Echogenic tip: Enhances visibility under ultrasound guidance (especially in EUS-guided procedures).
Protective sheath: Allows safe insertion and withdrawal through the endoscope’s working channel.
Available in various gauges: Commonly 19G, 22G, or 25G, to balance sample quality and flexibility.
Uses:
Tissue sampling from lymph nodes, pancreatic cysts, or tumors (for cytology/histology).
Commonly used in Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) or ERCP.
Can also aspirate fluid collections or drain cysts.
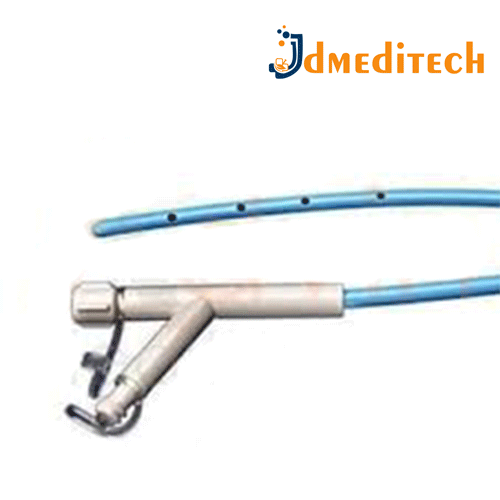
A Biliary Dilator is a medical device used to gradually enlarge or open narrowed sections (strictures) of the bile ducts during procedures like ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) or PTBD (Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage).
Key Features:
Tapered, flexible shaft: Allows smooth and safe navigation
Radiopaque markings: Assist with precise placement under imaging
Available in graded sizes: Enables stepwise dilation
Made of medical-grade plastic or metal: Ensures durability and safety
Compatible with guide wires: For accurate positioning
Uses:
Dilation of biliary strictures (benign or malignant)
Facilitating stent or catheter insertion
Pre-dilation before balloon or stent placement
Used in both endoscopic and percutaneous biliary procedures
A Biliary Balloon Dilator is a medical device used to dilate strictures (narrowed areas) or open blocked bile ducts during biliary procedures, especially in ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography).
Key Features:
High-pressure balloon: Inflates to dilate strictures effectively
Radiopaque markers: For precise positioning under fluoroscopy
Flexible catheter shaft: Allows smooth navigation into ducts
Various sizes: Tailored to different duct diameters and clinical needs
Uses:
Dilation of biliary strictures (benign or malignant)
Facilitating stent placement in bile ducts
Removing stones or debris by widening the bile duct opening
An Esophageal Balloon Dilator is a medical device used to gently expand narrowed areas of the esophagus (esophageal strictures). It is commonly used during endoscopy procedures to treat conditions that cause difficulty in swallowing.
Key Features:
Inflatable Balloon: Allows precise, controlled dilation.
Various Sizes: Comes in different diameters for gradual dilation.
Radiopaque Markers: Aid in accurate positioning under imaging.
Flexible Design: Minimizes trauma to esophageal tissue.
Use:
Dilates strictures caused by scarring, tumors, or inflammation.
Used in conditions like achalasia, esophagitis, or post-surgical narrowing.
Helps restore normal swallowing function.
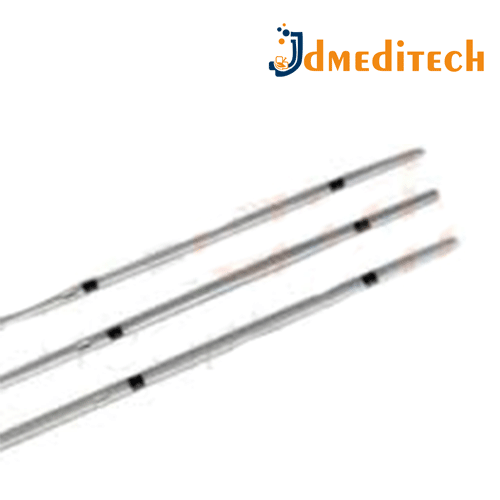
A Gastrology Nitinol Guide Wire is a flexible, high-performance wire used in gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures to assist in the navigation and placement of medical devices such as catheters, stents, or dilators.
Features:
Nitinol core: Offers superior flexibility, kink resistance, and shape memory.
Hydrophilic or PTFE-coated: Facilitates smooth and atraumatic advancement.
Radiopaque tip: Allows visualization under fluoroscopy for precise positioning.
Soft tip design: Minimizes trauma to delicate GI tissues.
Uses:
Assists in accessing strictures or obstructed ducts.
Guides instruments during ERCP, dilation, stent placement, or foreign body retrieval in the GI tract.